The only force acting on a 2.0 kg canister presents a captivating exploration into the realm of force dynamics. This force, acting upon the canister, propels it through space, shaping its motion and influencing its trajectory. As we delve into this intriguing subject, we will unravel the intricacies of force calculations, examine the effects of force on the canister’s motion, and uncover the practical applications of force analysis in canister design.
Force, a fundamental concept in physics, exerts a profound influence on objects within our world. It possesses the ability to alter an object’s state of motion, whether at rest or in motion. In the case of our 2.0 kg canister, a solitary force governs its movement, dictating its path and speed.
Forces Acting on a Canister
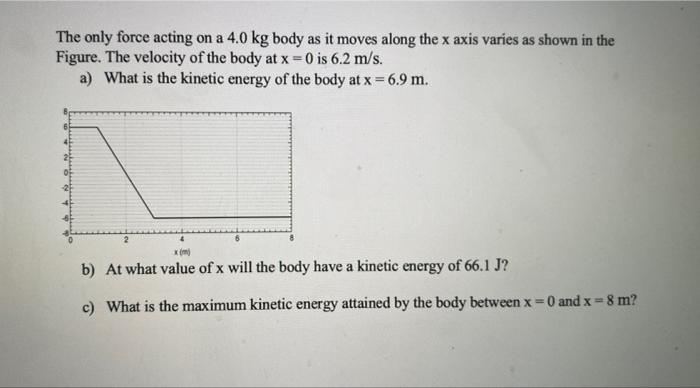
Forces are external influences that act upon objects, causing them to move, change shape, or deform. Understanding the forces acting on a canister is essential for analyzing its behavior and designing it to withstand various conditions.
Types of Forces Acting on a Canister, The only force acting on a 2.0 kg canister
- Gravity:The force exerted by the Earth’s mass on the canister, pulling it downwards.
- Normal Force:The force exerted by a surface that prevents the canister from sinking into it, acting perpendicular to the surface.
- Friction:The force that opposes the relative motion between two surfaces in contact, acting parallel to the surfaces.
- Air Resistance:The force exerted by air on the canister as it moves through the air, acting in the opposite direction of motion.
- Buoyancy:The upward force exerted by a fluid on a submerged or partially submerged object, equal to the weight of the fluid displaced by the object.
Force Calculations

The net force acting on an object is the vector sum of all forces acting on it. To calculate the net force, the following formula is used:
Fnet= F 1+ F 2+ … + F n
where F netis the net force, and F 1, F 2, …, F nare the individual forces acting on the object.
The direction of the net force is determined by the vector sum of the individual forces. The magnitude of the net force is the resultant force that causes the object to accelerate.
Step-by-Step Guide to Calculating the Net Force on a Canister
- Identify all the forces acting on the canister.
- Determine the direction and magnitude of each force.
- Sum the forces in each direction (x- and y-directions) to get the net force components.
- Use the Pythagorean theorem to find the magnitude of the net force.
- Use trigonometry to determine the direction of the net force.
Effects of Force on a Canister

The force acting on a canister can affect its motion in several ways:
- Linear Acceleration:A net force in the direction of motion will cause the canister to accelerate linearly.
- Rotational Acceleration:A net force acting at a distance from the canister’s center of mass will cause it to rotate.
- Deformation:A force that exceeds the canister’s structural strength can cause it to deform or break.
The relationship between force, mass, and acceleration is described by Newton’s second law of motion:
F = ma
where F is the net force, m is the mass of the object, and a is the acceleration.
Applications of Force in Canister Design
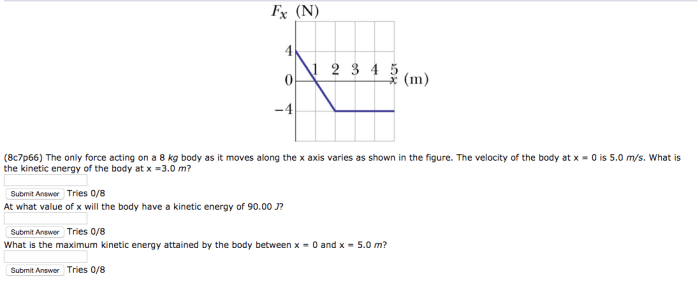
Understanding the forces acting on a canister is crucial in its design to withstand specific conditions:
- Impact Resistance:Designing canisters to withstand impacts involves analyzing the forces generated during impact and ensuring the canister’s structure can absorb or dissipate those forces.
- Pressure Resistance:Canisters designed to withstand high pressure must be able to resist the forces exerted by the internal pressure, which can cause deformation or rupture.
- Corrosion Resistance:Canisters exposed to corrosive environments require materials and coatings that can withstand the forces exerted by the corrosive agents.
Force analysis is used to optimize canister performance by:
- Determining the minimum material thickness required to withstand the expected forces.
- Designing reinforcements or support structures to enhance the canister’s strength.
- Selecting materials with specific properties to resist the anticipated forces.
Answers to Common Questions: The Only Force Acting On A 2.0 Kg Canister
What is the formula for calculating the net force acting on an object?
The formula for calculating the net force (F) acting on an object is: F = ma, where ‘m’ represents the mass of the object and ‘a’ represents its acceleration.
How does force affect the motion of a canister?
Force can influence the motion of a canister in various ways. It can cause the canister to accelerate, decelerate, or change its direction of motion. The magnitude and direction of the force determine the specific effect on the canister’s motion.
How is force analysis used in canister design?
Force analysis plays a crucial role in canister design. Engineers use force analysis to determine the forces acting on the canister during different scenarios, such as transportation, storage, or use. This analysis helps them design canisters that can withstand specific forces and maintain their integrity.
