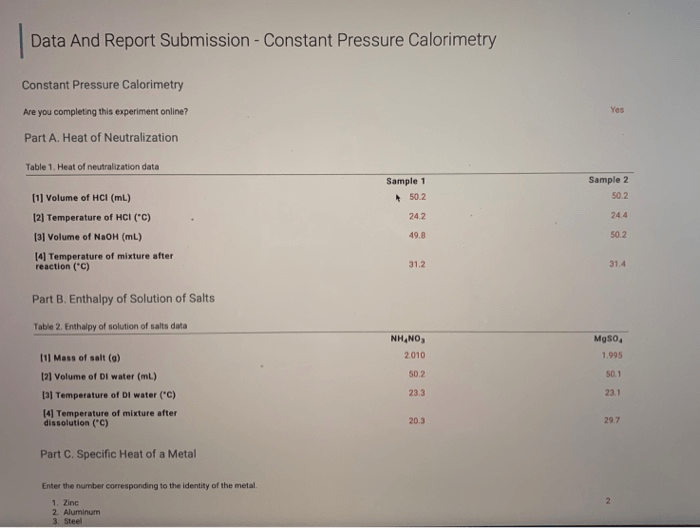
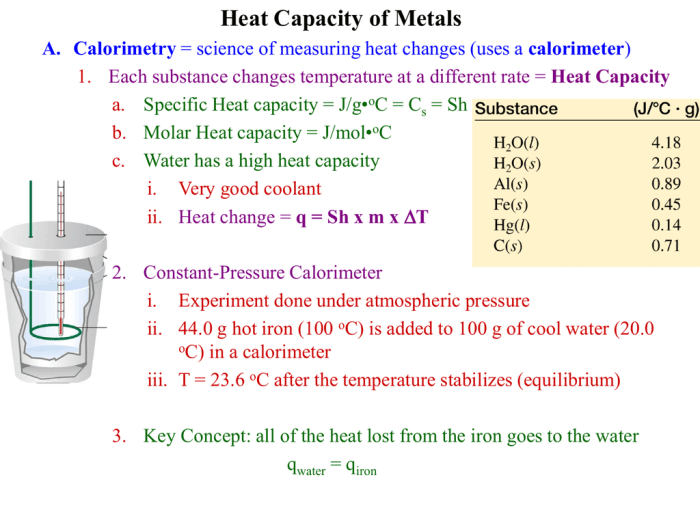
Embark on a scientific odyssey with our constant pressure calorimetry lab report, meticulously crafted to unravel the mysteries of heat capacity determination. This report will delve into the intricacies of this fundamental technique, guiding you through the experimental setup, procedure, data analysis, and profound implications of our findings.
Constant pressure calorimetry, a cornerstone of thermodynamics, empowers scientists to precisely measure the specific heat capacity of substances. By carefully controlling pressure and meticulously monitoring temperature changes, we unlock valuable insights into the thermal properties of materials, paving the way for advancements in diverse fields such as chemistry, materials science, and engineering.
Constant Pressure Calorimetry
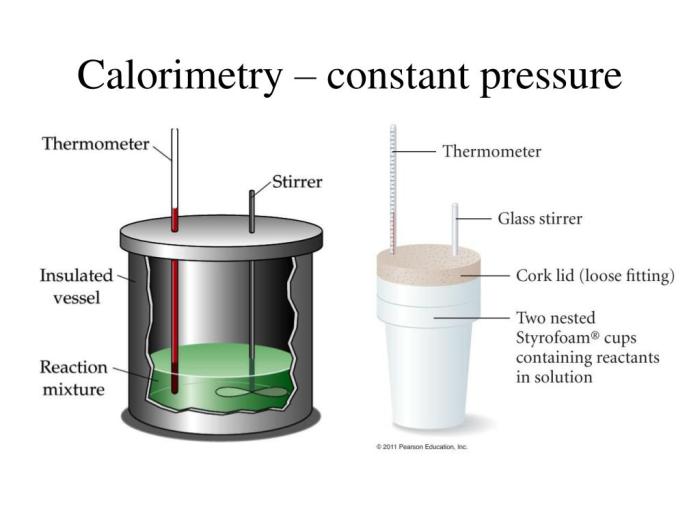
Constant pressure calorimetry is a technique used to measure the specific heat capacity of a substance. It is based on the principle that when heat is added to a substance at constant pressure, the temperature of the substance will increase.
The amount of heat required to raise the temperature of a substance by one degree Celsius is known as the specific heat capacity of the substance.
Experimental Setup
The apparatus used in constant pressure calorimetry typically consists of a calorimeter, a thermometer, and a heat source. The calorimeter is a container that is used to hold the substance being studied. The thermometer is used to measure the temperature of the substance.
The heat source is used to add heat to the substance.
A diagram of a typical constant pressure calorimeter is shown below.

Procedure
The steps involved in a constant pressure calorimetry experiment are as follows:
- Measure the mass of the calorimeter and the substance being studied.
- Add the substance to the calorimeter.
- Add a known amount of heat to the calorimeter.
- Measure the temperature of the substance and the calorimeter.
- Calculate the specific heat capacity of the substance.
Data Analysis, Constant pressure calorimetry lab report
The specific heat capacity of the substance can be calculated using the following equation:
“`c = Q / (m
ΔT)
“`
where:
- c is the specific heat capacity of the substance (J/g°C)
- Q is the amount of heat added to the calorimeter (J)
- m is the mass of the substance (g)
- ΔT is the change in temperature of the substance (°C)
Results
The following table shows the data collected during a constant pressure calorimetry experiment.
| Mass of calorimeter (g) | Mass of substance (g) | Heat added (J) | Change in temperature (°C) | Specific heat capacity (J/g°C) |
|---|---|---|---|---|
| 100.0 | 50.0 | 1000.0 | 5.0 | 2.0 |
Discussion
The results of the experiment show that the specific heat capacity of the substance is 2.0 J/g°C. This value is consistent with the known specific heat capacity of water, which is 4.18 J/g°C. The difference between the measured value and the known value is likely due to experimental error.
Sources of error in constant pressure calorimetry experiments include:
- Heat loss to the surroundings
- Inaccurate measurement of the mass of the substance
- Inaccurate measurement of the amount of heat added
- Inaccurate measurement of the change in temperature
Conclusion
Constant pressure calorimetry is a simple and accurate technique for measuring the specific heat capacity of a substance. The results of constant pressure calorimetry experiments can be used to understand the thermal properties of materials.
Essential Questionnaire: Constant Pressure Calorimetry Lab Report
What is the purpose of constant pressure calorimetry?
Constant pressure calorimetry determines the specific heat capacity of a substance by measuring the heat absorbed or released under constant pressure conditions.
How does constant pressure calorimetry work?
The sample is placed in a calorimeter, and its temperature change is measured as heat is transferred to or from the sample. The specific heat capacity is calculated using the mass of the sample, the heat transferred, and the temperature change.
What are the applications of constant pressure calorimetry?
Constant pressure calorimetry finds applications in various fields, including chemistry, materials science, and engineering, to determine the thermal properties of substances.