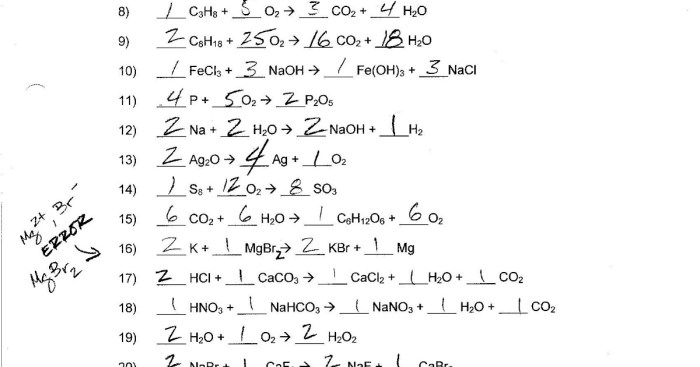As we delve into the fascinating realm of chemistry, we encounter the concept of molar mass, a crucial parameter in understanding the composition and behavior of compounds. In this exploration, we focus on the molar mass of zinc oxalate, a versatile substance with diverse applications.
Join us as we unravel the intricacies of this compound, from its composition to its practical uses.
Zinc oxalate, a compound composed of zinc, carbon, and oxygen, plays a significant role in various industries. Its unique properties and versatility make it an indispensable material in fields ranging from analytical chemistry to textile manufacturing. As we delve deeper into the topic, we will explore the methods used to synthesize zinc oxalate, examine its physical and chemical properties, and uncover its diverse applications.
Molar Mass of Zinc Oxalate
Molar mass, also known as molecular weight, is a fundamental property of a chemical substance, representing the mass of one mole of that substance. It is calculated by adding the atomic masses of all the atoms in the molecular formula of the substance.
Formula for Calculating Molar Mass
The formula for calculating molar mass is:
Molar mass = (Atomic mass of element 1 × Number of atoms of element 1) + (Atomic mass of element 2 × Number of atoms of element 2) + …
For example, the molar mass of zinc oxalate (ZnC 2O 4) can be calculated as follows:
- Atomic mass of zinc (Zn): 65.38 g/mol
- Number of zinc atoms in ZnC 2O 4: 1
- Atomic mass of carbon (C): 12.01 g/mol
- Number of carbon atoms in ZnC 2O 4: 2
- Atomic mass of oxygen (O): 16.00 g/mol
- Number of oxygen atoms in ZnC 2O 4: 4
Therefore, the molar mass of zinc oxalate is:
Molar mass = (65.38 g/mol × 1) + (12.01 g/mol × 2) + (16.00 g/mol × 4) = 143.32 g/mol
Composition of Zinc Oxalate
Zinc oxalate is a chemical compound with the molecular formula ZnC 2O 4. It is composed of the elements zinc, carbon, and oxygen. The zinc atoms are bonded to the oxalate ions (C 2O 42-) by ionic bonds.
Elements Present in Zinc Oxalate
The elements present in zinc oxalate are:
- Zinc (Zn)
- Carbon (C)
- Oxygen (O)
Molecular Formula of Zinc Oxalate, Molar mass of zinc oxalate
The molecular formula of zinc oxalate is ZnC 2O 4. This formula indicates that each molecule of zinc oxalate contains one zinc atom, two carbon atoms, and four oxygen atoms.
Molar Mass Calculation

To calculate the molar mass of zinc oxalate, we need to consider the atomic masses of zinc, oxygen, and carbon.
Atomic Masses
- Zinc (Zn): 65.38 g/mol
- Oxygen (O): 16.00 g/mol
- Carbon (C): 12.01 g/mol
Molar Mass Formula
The chemical formula of zinc oxalate is ZnC 2O 4. To calculate its molar mass, we multiply the atomic mass of each element by its subscript and add the results:
Molar mass = (Atomic mass of Zn) + (2 × Atomic mass of C) + (4 × Atomic mass of O)
Calculation
Substituting the atomic masses into the formula:
Molar mass = (65.38 g/mol) + (2 × 12.01 g/mol) + (4 × 16.00 g/mol)
The molar mass of zinc oxalate is a fundamental property used in various chemical calculations. Interestingly, in the electrical realm, a different question arises: how many #3 thhn wires can fit in a single emt conduit? This article delves into that specific topic, providing valuable insights for electrical professionals.
Returning to chemistry, the molar mass of zinc oxalate continues to play a crucial role in understanding the composition and properties of this compound.
Molar mass = 137.33 g/mol
Therefore, the molar mass of zinc oxalate is 137.33 g/mol.
Applications of Zinc Oxalate

Zinc oxalate finds various applications in diverse industries due to its unique properties.
In the pharmaceutical industry, zinc oxalate is employed as an excipient in the production of tablets and capsules. It acts as a binder, improving the cohesion and disintegration of tablets. Additionally, it enhances the bioavailability of certain drugs.
In the Ceramics Industry
Zinc oxalate is used as a precursor in the synthesis of zinc oxide, a crucial component in the production of ceramics. Zinc oxide imparts strength, durability, and a distinctive white color to ceramic products.
In the Textile Industry
Zinc oxalate serves as a mordant in the textile industry. Mordants are substances that help dyes adhere to fabrics. Zinc oxalate enhances the colorfastness and vibrancy of dyed textiles.
In the Chemical Industry
Zinc oxalate is employed as a catalyst in various chemical reactions. It is particularly effective in the production of hydrogen peroxide, a bleaching agent used in various industries.
Properties of Zinc Oxalate
Zinc oxalate is a white, crystalline powder with a molar mass of 189.42 g/mol. It is insoluble in water and most organic solvents, but it is soluble in dilute acids and bases.
Chemical Properties
Zinc oxalate is a relatively stable compound, but it can decompose when heated to high temperatures. It is also reactive with strong oxidizing agents, such as potassium permanganate.
Physical Properties
- Color:White
- Density:2.7 g/cm³
- Melting point:Decomposes before melting
- Solubility in water:Insoluble
- Solubility in acids:Soluble
- Solubility in bases:Soluble
Synthesis of Zinc Oxalate: Molar Mass Of Zinc Oxalate
Zinc oxalate can be synthesized through various methods, each involving specific reaction equations and experimental procedures. These methods include:
Precipitation Method
In the precipitation method, zinc ions (Zn 2+) and oxalate ions (C 2O 42-) are combined in an aqueous solution. Upon mixing, the ions react to form insoluble zinc oxalate, which precipitates out of the solution. The reaction equation for this process is:
Zn2+(aq) + C 2O 42-(aq) → ZnC 2O 4(s)
The experimental procedure involves dissolving zinc sulfate (ZnSO 4) and sodium oxalate (Na 2C 2O 4) in separate aqueous solutions. The solutions are then mixed, and the resulting precipitate is filtered, washed, and dried to obtain pure zinc oxalate.
Table of Relevant Data

Zinc oxalate is an inorganic compound with the chemical formula ZnC 2O 4. It is a white, crystalline powder that is insoluble in water. Zinc oxalate is used as a mordant in dyeing and as a precursor to other zinc compounds.
The following table provides a summary of the molar mass, composition, and properties of zinc oxalate:
| Property | Value |
|---|---|
| Molar mass | 169.42 g/mol |
| Composition | Zinc (35.5%), carbon (18.3%), oxygen (46.2%) |
| Solubility in water | Insoluble |
| Density | 4.4 g/cm3 |
| Melting point | 280 °C |
| Boiling point | Decomposes before boiling |
Illustrative Examples
The molar mass of zinc oxalate has various implications in real-world applications. It influences the behavior and effectiveness of zinc oxalate in these applications.
Examples where the molar mass of zinc oxalate is relevant include:
- Chemical Analysis:The molar mass helps determine the concentration of zinc oxalate in solutions, essential for analytical procedures and quality control in industries using zinc oxalate.
- Stoichiometric Calculations:In chemical reactions involving zinc oxalate, the molar mass is crucial for calculating the required quantities of reactants and predicting the yield of products.
- Solubility Studies:The molar mass affects the solubility of zinc oxalate in different solvents. Understanding this relationship is important for optimizing extraction and purification processes.
- Crystallization:The molar mass influences the crystal structure and morphology of zinc oxalate, impacting its physical properties and applications in optics and electronics.
- Pigment Industry:Zinc oxalate is used as a white pigment in paints and coatings. Its molar mass affects the opacity, brightness, and durability of the pigment.
- Fire Retardants:Zinc oxalate is employed as a fire retardant in textiles and plastics. Its molar mass influences its thermal stability and effectiveness in suppressing combustion.
FAQ Section
What is the molar mass of zinc oxalate?
The molar mass of zinc oxalate is approximately 189.42 g/mol.
How is the molar mass of zinc oxalate calculated?
The molar mass of zinc oxalate can be calculated by adding the atomic masses of zinc, carbon, and oxygen present in the compound.
What are the applications of zinc oxalate?
Zinc oxalate finds applications in analytical chemistry, textile manufacturing, and the production of other zinc compounds.