Commodification definition ap human geography – As the concept of commodification takes center stage in AP Human Geography, this exploration delves into its intricacies, examining how objects and experiences are transformed into commodities within the human landscape. From historical examples to contemporary manifestations, we unravel the social, economic, and ethical implications of this pervasive process.
Throughout this discourse, we will trace the historical trajectory of commodification, identifying key turning points and the driving forces behind them. We will also analyze contemporary examples, scrutinizing the impact of commodification on society and the economy. Finally, we will speculate on the future of commodification, considering how technological advancements and other factors may shape its evolution.
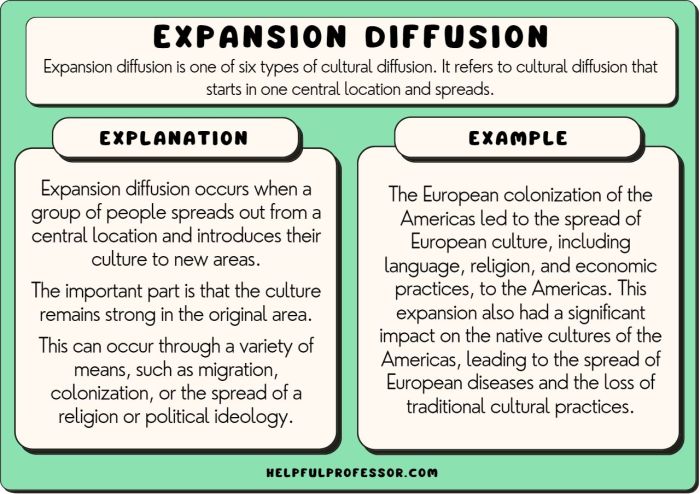
Definition of Commodification
Commodification is the process of transforming something into a commodity, which is an object that can be bought and sold in a market. In human geography, commodification refers to the process of turning things that were once considered to be outside the market economy into commodities that can be bought and sold.
There are many different ways in which things can become commodified. One common way is through the process of privatization, in which things that were once owned in common by a group of people become owned by individuals. Another way is through the process of commercialization, in which things that were once produced for non-market purposes become produced for sale in a market.
Historical Examples of Commodification
There are many historical examples of how things have been commodified over time. One example is the commodification of land, which began in Europe in the 16th century. Before this time, land was typically owned by communities or by the state.
However, with the rise of capitalism, land began to be bought and sold as a commodity, which led to the enclosure of common lands and the displacement of many rural people.
Another example of commodification is the commodification of labor, which began in the 18th century with the rise of industrial capitalism. Before this time, most people worked on farms or in small businesses. However, with the rise of factories, people began to be employed as wage laborers, which meant that they sold their labor power to employers in exchange for wages.
Contemporary Examples of Commodification, Commodification definition ap human geography
There are many contemporary examples of how things are being commodified. One example is the commodification of water, which has become increasingly common in recent years as a result of the global water crisis. Water is now being bought and sold as a commodity on the international market, which has led to price increases and shortages in many parts of the world.
Another example of commodification is the commodification of education, which has become increasingly common in recent years as a result of the rise of the global knowledge economy. Education is now being bought and sold as a commodity on the international market, which has led to increased costs and inequality in access to education.
Pros and Cons of Commodification
There are both advantages and disadvantages to commodification. On the one hand, commodification can lead to increased efficiency and productivity, as it allows for the specialization of production and the division of labor. Commodification can also lead to increased innovation, as it provides incentives for people to develop new products and services.
On the other hand, commodification can also lead to a number of negative consequences, such as increased inequality, as it can lead to the concentration of wealth in the hands of a few people. Commodification can also lead to the destruction of traditional cultures and values, as it can lead to the replacement of traditional ways of life with market-oriented values.
Future of Commodification
It is difficult to say what the future of commodification will be. However, it is likely that commodification will continue to increase in the years to come, as the global economy becomes increasingly interconnected and market-oriented. This could lead to a number of positive and negative consequences, and it is important to be aware of these consequences so that we can make informed decisions about how we want to shape the future of commodification.
Essential Questionnaire: Commodification Definition Ap Human Geography
What is the definition of commodification in human geography?
Commodification in human geography refers to the process by which objects, experiences, or even human relationships are transformed into commodities that can be bought and sold in the marketplace.
What are some historical examples of commodification?
Historical examples of commodification include the commodification of land during the enclosure movement in England, the commodification of labor during the Industrial Revolution, and the commodification of natural resources during the colonial era.
What are some contemporary examples of commodification?
Contemporary examples of commodification include the commodification of education, healthcare, and even personal data.
What are the pros and cons of commodification?
Pros of commodification include increased efficiency, innovation, and economic growth. Cons of commodification include social inequality, environmental degradation, and the erosion of traditional values.
What is the future of commodification?
The future of commodification is uncertain, but it is likely that technological advancements and other factors will continue to shape the way in which objects, experiences, and human relationships are transformed into commodities.