Identify each of the following structures as haploid or diploid. – In the realm of cell biology, understanding the distinction between haploid and diploid structures is paramount. Haploid and diploid cells possess unique characteristics that significantly impact the life cycle of organisms. This article delves into the intricacies of these cellular states, exploring their significance and the processes that govern their formation.
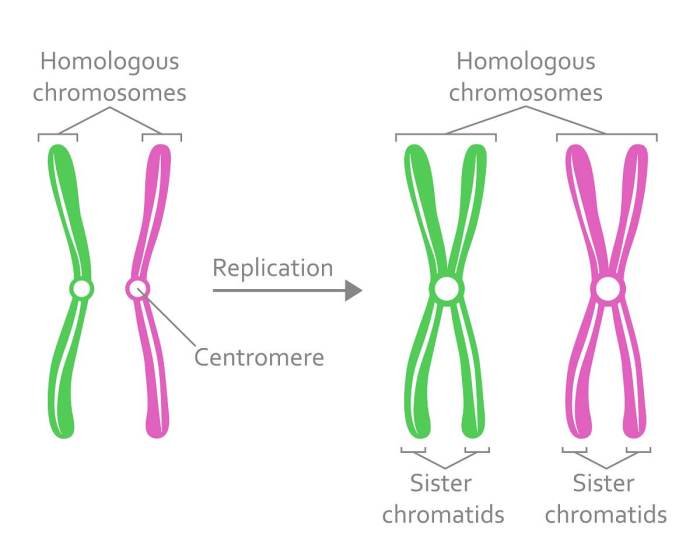
Haploid cells, characterized by a single set of chromosomes, contrast with diploid cells, which possess two sets. These variations have profound implications for genetic diversity, reproduction, and the overall functioning of living organisms.
Types of Cells: Identify Each Of The Following Structures As Haploid Or Diploid.
Cells are the fundamental unit of life. They come in two main types: haploid and diploid.
Haploid cells contain a single set of chromosomes, while diploid cells contain two sets of chromosomes.
Examples of Haploid Cells
- Sperm cells
- Egg cells
- Pollen grains
Examples of Diploid Cells
- Body cells
- Somatic cells
- Zygotes
Significance of Haploidy and Diploidy
Haploidy and diploidy play important roles in the life cycle of organisms. Haploid cells are involved in sexual reproduction, while diploid cells are involved in asexual reproduction.
Meiosis and Mitosis
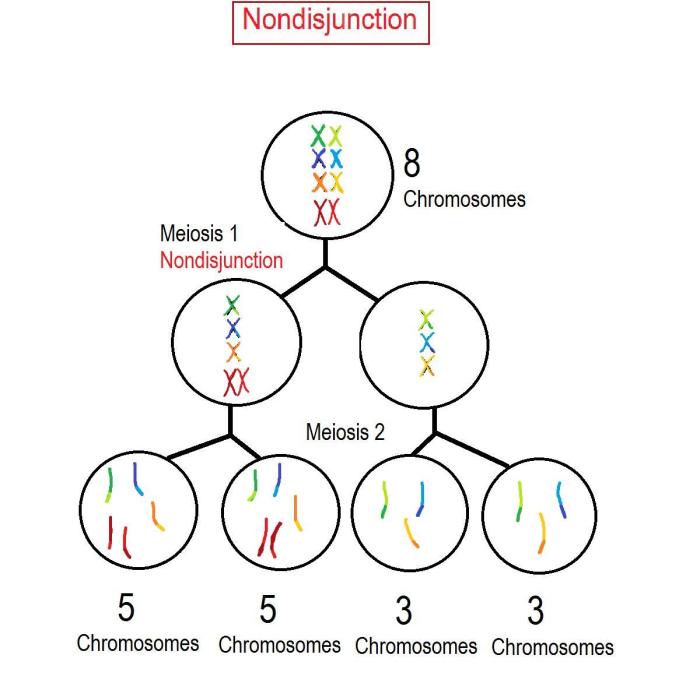
Meiosis
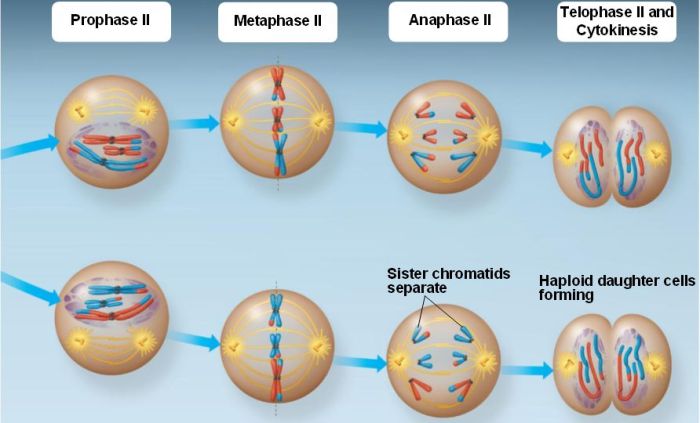
Meiosis is a type of cell division that produces haploid cells. It occurs in the reproductive organs of organisms.
During meiosis, the chromosomes are duplicated and then divided into four haploid cells.
Mitosis
Mitosis is a type of cell division that produces diploid cells. It occurs in the body cells of organisms.
During mitosis, the chromosomes are duplicated and then divided into two diploid cells.
Key Differences between Meiosis and Mitosis
| Characteristic | Meiosis | Mitosis |
|---|---|---|
| Number of cell divisions | Two | One |
| Number of daughter cells | Four | Two |
| Chromosome number in daughter cells | Haploid | Diploid |
| Function | Sexual reproduction | Asexual reproduction |
Fertilization
Fertilization is the process of combining a haploid sperm cell with a haploid egg cell to form a diploid zygote.
Fertilization occurs in the reproductive organs of organisms.
Importance of Fertilization
Fertilization is essential for the life cycle of organisms. It produces a diploid zygote, which develops into a new organism.
Exceptions to the Haploid/Diploid Rule
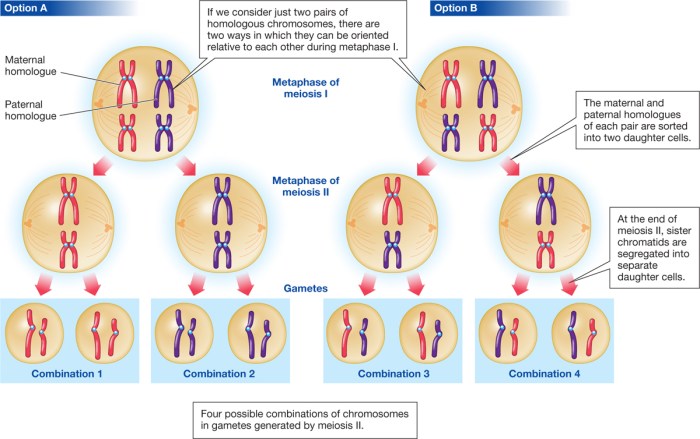
There are a few exceptions to the haploid/diploid rule.
Examples of Exceptions
- Some organisms, such as roundworms, have haploid body cells.
- Some organisms, such as bees, have diploid males.
- Some organisms, such as plants, have both haploid and diploid phases in their life cycle.
Reasons for Exceptions, Identify each of the following structures as haploid or diploid.
The reasons for these exceptions are not fully understood. However, it is thought that they may be due to evolutionary adaptations.
Implications for Cell Biology
These exceptions to the haploid/diploid rule challenge our understanding of cell biology. They suggest that the haploid/diploid rule is not as universal as once thought.
Key Questions Answered
What is the significance of haploidy in sexual reproduction?
Haploid cells, with their reduced chromosome number, facilitate the process of genetic recombination during sexual reproduction. By combining genetic material from two haploid gametes, offspring inherit a unique blend of traits, enhancing genetic diversity and adaptability.
How does meiosis contribute to the formation of haploid cells?
Meiosis, a specialized cell division process, reduces the chromosome number by half, resulting in the production of haploid cells. This process is crucial for the formation of gametes (eggs and sperm) in sexually reproducing organisms.
What are the key differences between haploid and diploid cells?
Haploid cells contain a single set of chromosomes, while diploid cells possess two sets. Haploid cells are typically produced through meiosis, whereas diploid cells result from fertilization or mitosis. Haploid cells are commonly found in gametes, while diploid cells are prevalent in somatic cells.