Teradata no more spool space: a common error that can halt your data processing operations. In this comprehensive guide, we’ll delve into the causes, management strategies, and resolution techniques for this frustrating issue, empowering you to optimize your Teradata environment and keep your data flowing smoothly.
Spool space plays a crucial role in Teradata’s data processing engine. It’s a temporary storage area that holds intermediate results during query execution. When spool space runs out, queries can fail, leading to disruptions and delays.
Understanding Spool Space in Teradata
Spool space is a crucial component in Teradata, serving as a temporary storage area for data during query processing. It enables efficient handling of large data volumes, facilitating complex computations and ensuring optimal performance.Spool space is primarily used to store intermediate results during query execution, allowing Teradata to break down complex queries into smaller, manageable chunks.
This approach reduces the memory footprint of the query, preventing system overloads and enabling the processing of larger datasets.
Types of Spool Space
Teradata offers two types of spool space:
- Global Spool Space:Shared by all users and queries, providing a centralized pool of resources. It is suitable for smaller queries or queries with predictable spool space requirements.
- Private Spool Space:Allocated to individual users or queries, offering dedicated resources. This option is beneficial for large queries or queries with highly variable spool space consumption.
Factors Affecting Spool Space Consumption
Several factors can influence spool space consumption, including:
- Query Complexity:Complex queries involving joins, subqueries, or aggregations require more spool space to store intermediate results.
- Data Volume:The amount of data processed by the query directly impacts spool space consumption.
- Data Types:Data types with larger sizes, such as CLOBs or BLOBs, occupy more spool space.
- Query Optimization:Poorly optimized queries can result in inefficient spool space utilization.
Causes of No More Spool Space Errors

No more spool space errors in Teradata occur when the system runs out of space to store intermediate data during query execution. This can happen due to several common causes:
Excessive Data Processing or Complex Queries
When queries involve large amounts of data or complex operations, such as aggregations, joins, or sorting, they can consume a significant amount of spool space. If the query exceeds the available spool space, the system will raise a “no more spool space” error.
Concurrent User Sessions and Data Loads
In a multi-user environment, multiple concurrent user sessions can contribute to spool space exhaustion. Each user’s queries and data loads consume spool space, and if the combined usage exceeds the available capacity, errors can occur. Similarly, large data loads can also temporarily deplete spool space, leading to errors if other operations are running concurrently.
If you’re struggling with Teradata’s “no more spool space” error, consider checking out unit 4 session 5 letrs for insights and potential solutions. While it may seem unrelated, this resource offers valuable tips that can help you resolve the issue and improve your Teradata experience.
Managing Spool Space Usage
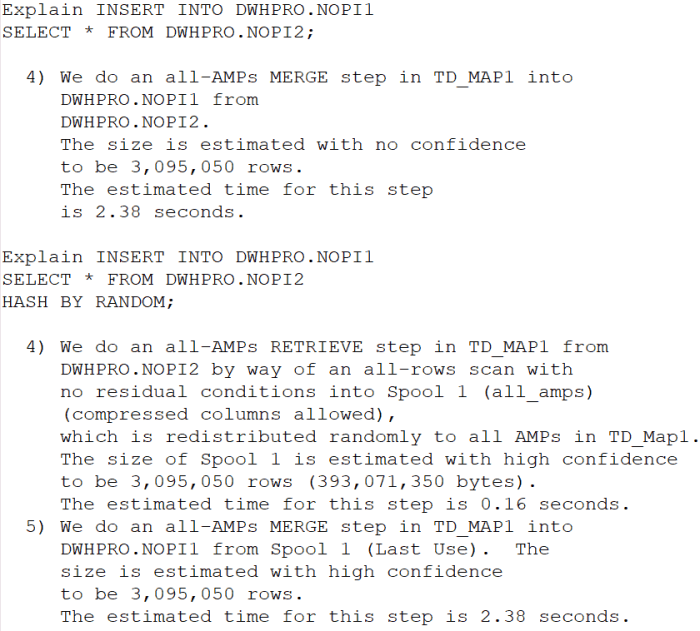
To optimize spool space utilization, it’s crucial to adopt effective strategies. Monitoring spool space usage helps identify potential bottlenecks, while techniques like query optimization and limiting data loads can significantly reduce consumption.
Monitoring Spool Space Usage
Regularly monitoring spool space usage is essential. Teradata provides various tools, such as the DBS Control utility and SQL queries, to track spool space consumption and identify trends.
- DBS Control: The DBS Control utility offers a graphical interface to monitor spool space usage in real-time. It provides detailed information on spool space allocation and usage by different sessions and queries.
- SQL Queries: SQL queries can be used to retrieve spool space usage data. For example, the following query displays the spool space usage for all sessions:
SELECT DBS_SPOOL_SPACE_USED() AS spool_space_used;
Optimizing Query Execution
Optimizing query execution can significantly reduce spool space consumption. Consider the following techniques:
- Use Indexes: Indexes help Teradata quickly locate data without scanning the entire table. This reduces the amount of data that needs to be spooled, resulting in lower spool space consumption.
- Optimize Query Structure: Avoid using complex subqueries and unnecessary joins. Break down complex queries into smaller, more efficient ones.
- Limit Data Retrieval: Use the LIMIT clause to restrict the number of rows retrieved by a query. This can significantly reduce spool space consumption, especially for large result sets.
Limiting Data Loads, Teradata no more spool space
Limiting data loads can help prevent spool space exhaustion. Consider the following strategies:
- Use Batch Processing: Break down large data loads into smaller batches. This reduces the amount of data that needs to be spooled at once, preventing spool space exhaustion.
- Use Direct Path Loads: Direct path loads bypass the spool space and directly load data into Teradata tables. This can significantly reduce spool space consumption for large data loads.
- Compress Data: Compressing data before loading it into Teradata can reduce the amount of spool space required.
Resolving No More Spool Space Errors

When encountering “no more spool space” errors, prompt action is necessary to resolve the issue and ensure seamless query execution. Here are the steps to follow:
- Identify the cause:Determine the specific operation or query that triggered the error. Check the query plan and identify areas with excessive spool space consumption.
- Increase spool space allocation:Contact your Teradata administrator to request an increase in the spool space allocation for your session or database. This will provide more temporary storage for intermediate query results.
- Use temporary tables:Create temporary tables to store intermediate results instead of using spool space. Temporary tables are stored in memory and released automatically at the end of the session, reducing spool space usage.
- Leverage external storage:Consider using external storage, such as Hadoop or Amazon S3, to store large intermediate results. This offloads data from the Teradata spool space, freeing up resources for other operations.
Best Practices for Spool Space Management
Effective spool space management is crucial to prevent “No More Spool Space” errors. Here are some best practices to ensure optimal utilization:
Regular monitoring and proactive planning are essential. Track spool space usage and project future needs to identify potential bottlenecks.
Use Automation Tools
Automation tools can streamline spool space management. Consider using scripts or third-party tools to automate tasks like spool space monitoring, threshold alerts, and cleanup processes.
FAQ Section: Teradata No More Spool Space
What is spool space in Teradata?
Spool space is a temporary storage area used to store intermediate results during query execution.
What are the common causes of “no more spool space” errors?
Excessive data processing, complex queries, concurrent user sessions, and large data loads can all contribute to spool space exhaustion.
How can I resolve “no more spool space” errors?
You can increase spool space allocation, use temporary tables or external storage to reduce spool space usage, and optimize queries to reduce data processing.
What are the best practices for managing spool space?
Regular monitoring, proactive planning, and the use of automation tools are essential for effective spool space management.